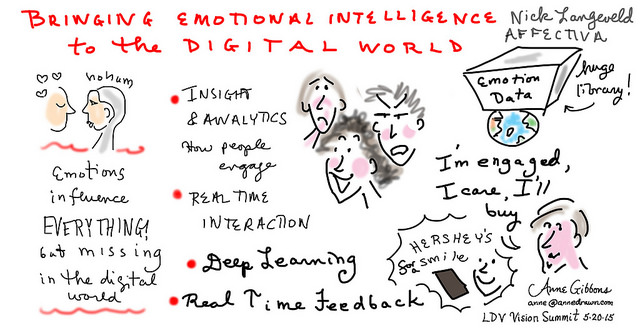
What is Emotional intelligence?
Emotional Intelligence (EI) is the ability to perceive, control and evaluate emotions. Researchers have suggested that emotional intelligence can be learned and strengthened, while others argue that it is an inborn characteristic. In the scholarly sphere, emotional intelligence is widely described as, “the subset of social intelligence that involves the ability to monitor one’s own and others’ feelings and emotions, to discriminate among them and to use this information to guide one’s thinking and actions.” In this regard, emotional intelligence is defined in different perspectives: perceived emotions, reasoning with emotions, understanding emotions, and managing emotions.
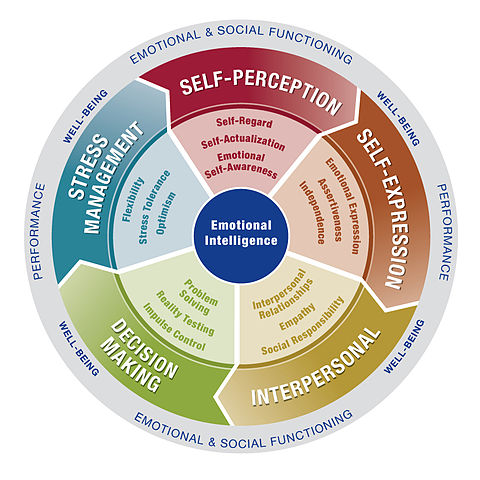
Reasoning with Emotions: This step involves the use of emotions to enhance the level of cognitive activity. On an individual level, emotions help people prioritize what they see and subsequently respond; we respond emotionally to things that catch our attention.
Understanding emotions: The emotions people perceive often carry a wide variety of meanings, most of which that are depicting a person expressing angry emotions, thus the observer need to interpret the cause of their anger.
Managing Emotions: This refers to the ability to manage emotions effectively as a key part towards emotional intelligence. Regulating personal emotions, responding appropriately and responding to the emotions is a very important aspect of emotional management.
All these factors contribute to a person’s capacity to perceive reason, understand and manage emotions culminating in the general description of being emotionally intelligent.